1. Introduction
In organizations, empowerment means granting employees the autonomy to assume a more active and responsible role. This is accomplished by strengthening their sense of effectiveness as well as by sharing power, information and the responsibility to manage their own work as much as possible. In terms of organizational culture, empowerment is related to the Individual Autonomy dimension.
But why should we empower our employees? Here are some benefits that empowerment may bring to organizations:
- Improves communication and decision making
- Improves morale, motivation and commitment
- Creates “ownership” of the job
- Increases job satisfaction
- Increases risk-taking and innovation
- Improves relationships with customers and suppliers
- Reduces layers of management
- Not everyone wants to be empowered
- We can not just empower staff and assume that they will assume the empowerment
- Empowerment may not be appropriate for some organizations
- Empowerment actually requires more management effort
- Empowerment means changes and constant changes may keep things unsettled
- There is a risk that empowerment efforts may fail
3. Barriers to empowerment
Here are some barriers that may prevent empowerment to be implemented:
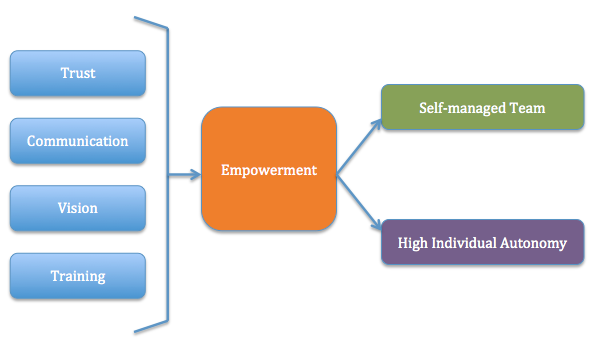
- Lack of trust between manager and staff
- No clear definition and policy about accountability
- Empowered staff do not receive enough training to be able to handle the empowerment
- No differentiation between staff
- Lack of communication
- Unclear vision
- Unwillingness to give up control
- Reluctance to change management style
- Fear of losing position
- Cling to old accountability
- Do not want to be accountable
- Do not realize their values and potentials
- Fear of losing position due to new accountability
- Lack of training
4. Implementing empowerment
By understanding possible barriers to empowerment, here are how empowerment can be implemented in organizations:
- Develop a clear mission and communicate it clearly to all employees
- Build trust within the organization at all levels
- Build an organizational culture that encourage innovation and risk taking
- Provide adequate training so that staff can handle the empowerment
- Replace hierarchical structure with self-managed teams
- Set clear boundaries for authority and accountability
- Get staff to involve in selecting their work assignments and the methods for accomplishing tasks
- Create and environment of cooperation, information sharing, discussion, and shared ownership of goals
- Encourage staff to take initiative, make decision, and use their knowledge
- When problems arise, find out what staff think and let them help design the solutions
- Stay out of the way, give staff the freedom to put their ideas and solutions into practice
- Maintain high morale and confidence by recognizing successes and encouraging high performance
In my opinion, empowerment should be compulsory in startup company and become part of its organizational culture for the following reasons:
- In terms of organizational culture, startup company should have high level of Individual Autonomy dimension and this can only be achieved via empowerment.
- Employees in startup company are usually the “A players” and they are likely to have the ability to handle empowerment.
- Startup company is there to grow fast and so are its employees. Empowerment will prepare and help them to grow.
- For startup software company, such Agile methodologies as Scrum or Extreme Programming requires self-managed teams and this can only be achieved via the implementation of empowerment.
Reference:
Bess, D., 2012. Power, BUS 626 Organizational Behavior. University of Hawaii at Manoa, unpublished.